Support and Resistance Indicators Trading Strategy Definition

Support and Resistance: Definition
Support and resistance levels are an integral part of any financial market. Market participants define these levels, which essentially represent supply and demand, or the flow of orders, which can shift rapidly. This is where bulls and bears resist, with one winning side always gaining the upper hand, one way or another. The price may react submissively or reactively to a price level where buyers or sellers are matched.
There are hundreds of methods to find support and resistance (S&R). If a trader decides to place all lines on the chart, he can't even see the price on the chart. Why? Because the price would simply disappear behind the lines. Of course, traders must choose the best S&R levels, otherwise the chart will become unreadable and useless.
So how can traders distinguish the most important levels? And above all, what should you consider important? S&R only becomes valuable when the market actually maintains the level in most cases. If a S&R level is used only occasionally or infrequently, a trader has no advantage in placing it in the chart.
In summary, traders look for the best and most respected S&R levels.
Every day, traders begin their trading journey in the world's largest financial market, the Forex market. Beginners want to take advantage of the enormous volatility of the average daily trading volume movements of $5.3 trillion. Traders who are new to the market are not expected to take bold steps, and those who do should only trade after a thorough analysis of the Forex market. The market has its own rhythm; it is better to identify the underlying movement of the pair and then act on it rather than trading on a gut feeling basis.
One of the most important types of analysis is technical analysis. This technical analysis starts from the assumption that "history repeats itself" and is based on the historical movement of the underlying currency pairs/shares/commodities, etc.
At the end of a thorough technical analysis, a trader derives important supports and resistances that should be considered when deciding on a trading opportunity. A good example of such a basic technical analysis tool is - " Fibonacci " - which is examined in this article along with several other ways to determine significant S&R values that may be useful for a beginner trader.
Psychological Support and Resistance Levels
Often the price tests certain psychological levels, and if the price ends with several 0's, these are often called "psychological" levels. People tend to move towards round numbers when discussing price levels, especially in forex trading. To illustrate that when traders discuss the future value of the euro, they are unlikely to give an answer such as 1.18732 or 1.20345. Instead, it is more likely that they will round their orders or price forecasts to something simpler such as 1.1800 or 1.2000.
Often we will see a number of orders around these large round numbers, resulting in a stronger level of S&R.
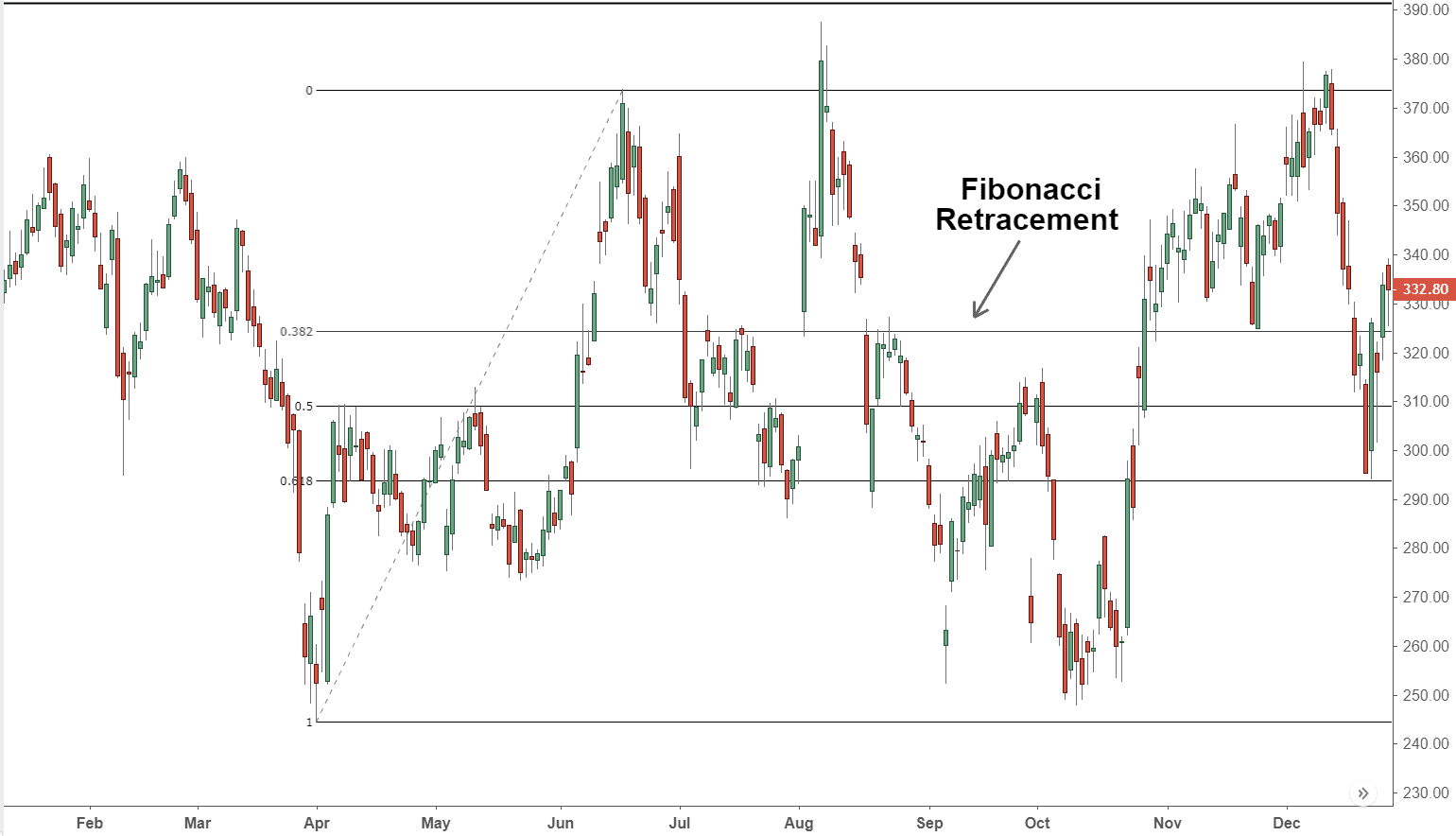
In addition, the more common psychic levels usually appear when the price has two zeros at the end, such as 1.1800 or 112.00. However, even more powerful psychic levels would end with three zeros, such as 1.2000 or 110.00. In addition, the most powerful psychological levels of all would end with four zeros, such as 1.0000 or 100.00. The following graphic shows four levels that are represented on different psychological levels. We can clearly see their effects on the price development.
How to Use Fibonacci Retracement with Support and Resistance
You may wonder how you can find Fibonacci's support and resistance in day trading. It should be an uncomplicated process. Fibonacci numbers, the great 13th century work of Italian mathematician Leonardo Fibonacci, were one of the most important secrets in the development of many technical indicators that helped to carry out precise technical analysis.
What is Fibonacci?
Fibonacci is a series of numbers that lead to a particular number by adding the two previous numbers, for example, 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, etc. These numbers are often used to calculate targets and entry points when trading stocks, commodities and especially forex during the trends that occur in the market. Remember that Fibonacci is only used in trend markets and should always move from left to right.
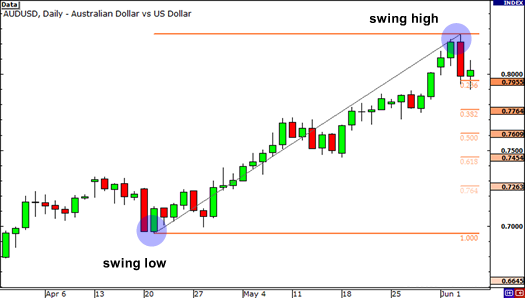
Fibonacci retracement numbers are used to indicate targets and entry points during trend markets. They signal the reversal points at which traders could find entry points during a retracement in a trend. In a downtrend, you draw Fibonacci levels from top to bottom (always from left to right).
In an uptrend, you draw Fibonacci values from bottom to top (always from left to right).
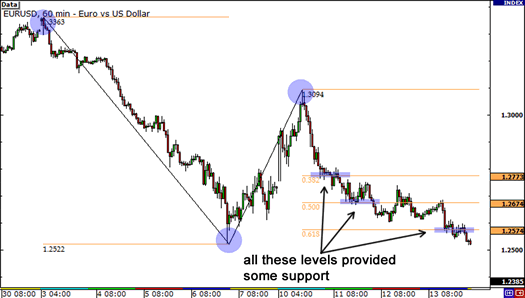
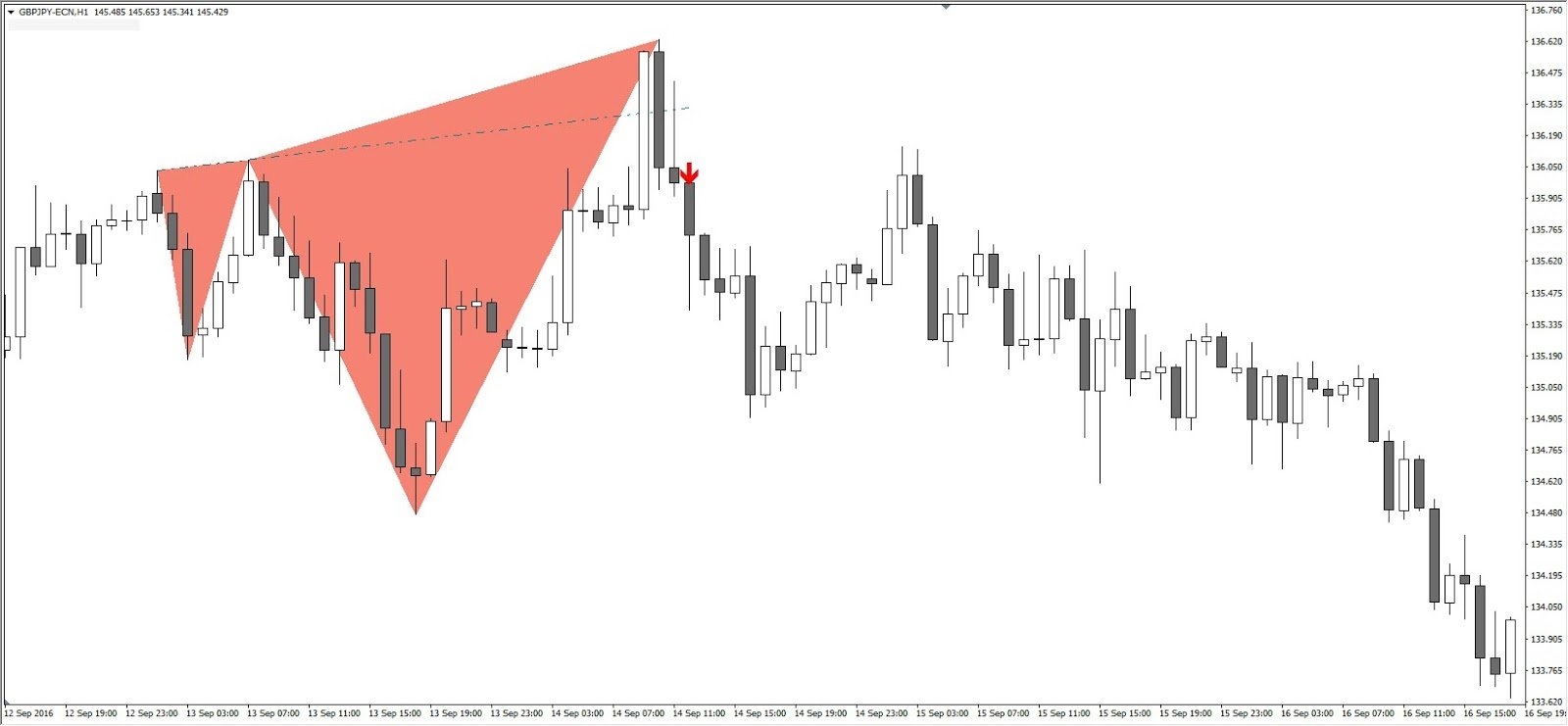
Fibonacci expansion/projection offers potential levels of profit taking once the starting point of the current movement has been tested and the price continues to trade in the same direction. Let's look at an example of an uptrend with the GBP/JPY shown above: (The Fibonacci expansion is shown in red)
The main objectives of the Fibonacci expansion are:
- 0.618 - FE 61.8
- 1 - FE 100,0
- 1,618 - FE 161,8
Wolfe Wave
Wolfe waves are a naturally occurring trading pattern found in all financial markets. Wolfe waves were originally discovered by an S&P500 trader named Bill Wolfe and work a bit like Elliott waves, although there are some differences in charting techniques. Patterns that are identified as Wolfe waves are natural and reliable reversal patterns that are present in all markets and time periods.
A Five-Wave Pattern
As the name suggests, this pattern consists of five waves that show supply and demand towards an equilibrium price. Wolfe waves usually develop in all time windows and are used to predict where the price will go and when it might arrive. When correctly identified, Wolfe waves can be used to accurately predict the size (equilibrium price) of the underlying security and to anticipate price reversals that are likely to cause large price fluctuations.
The most important thing is to identify the prevailing trend line and ensure that it has at least four points of contact. The next important factor is to locate a clear break in this trend line. Considering that reversals in the market only occur at 20%, the last high/low should be questioned. The Wolfe secret is to use this point for your trigger on the price pattern. The idea is that the prevailing trend line becomes a diagonal support/resistance line that you use to identify this entry point.
How to identify Wolfe Wave
The Wolfe wave consists of a 1-2-3-4-4-5 wave formation, where 2 and 4 refer to the retracement waves seen in the Wolfe wave formation. Wolfe wave traders distinguish between two different types of Wolfe waves - strict waves and modified waves.
Strict Wolfe waves are represented according to these rules:
- Waves 3-4 must remain within the channel created by 1-2;
- Wave 1-2 corresponds to waves 3-4;
- Shaft 4 lies between shafts 1 and 2;
- Between all shafts there is a regular distance;
- wave 5 crosses the trend line created by waves 1 and 3.
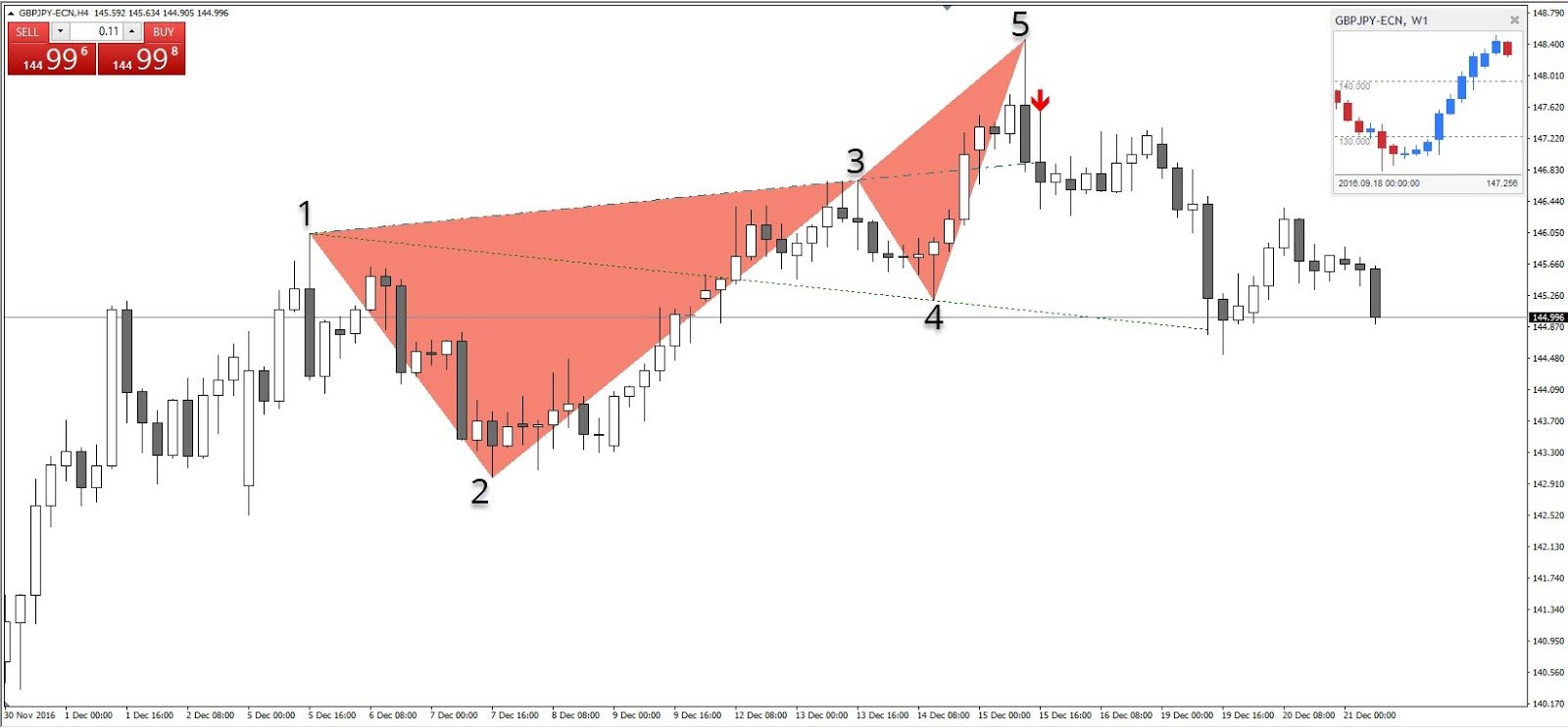
The main difference between strict and modified waves is that in a modified Wolfe wave, point 4 is within the channel created by waves 1-2.
Trigger: After the perceived Wolfe wave pattern is identified, place the Limit Order Trigger entry near the diagonal line resistance area of the price pattern. Normally trading will commence when the price closes above the trend line of waves 1 and 3.
Stop: The last high/low of the pattern.
Profit target: Point 5 is the trade entry point and is expected to hit the EPA (take profit point) by hitting a line drawn from point ,1, which also intersects with point 4. In the following example we can clearly see that the EPA (expected price at arrival) has been met and exceeded:
Camarilla Pivots
The most basic and simple definition of the camarilla is that it defines trend and margin. Traders can easily and quickly define whether a market is trending down, up or into the future by looking at the Camarilla indicator for a few seconds. Simply put, the Camarilla indicator provides valuable, simple and automated S&R levels.
The Camarilla is highly valued by professional traders. One of the main reasons is that institutional traders use it very intensively. The other reason is that the market naturally moves around the Camarilla values and uses them as a center or boundary for daily and weekly price actions.
Other advantages of Camarilla include
- It's automatically generated every trading day;
- That it requires no adjustment or manual work by the trader;
- That it keeps the chart simple with six baselines (3 red; 3 green).
Trend: The price is in trend mode when it is outside zones H3 and L3. That is, either above H3 for an uptrend or below L3 for a downtrend.
Range: The price is in a range mode when it is between zones H3 and L3.
Scalping with Camarilla Pivot
Camarilla can be traded as:
- S&R basics
- S&R breakout.
Scenario #1: The Market Opens Between H3 and L3 Levels
Shorts:
If the market opens between the H3 and L3 levels, you will have to wait until the price approaches one of these two levels. Potential trades can be made when the price reaches H3 or L3.
Bounce trade: If we want a short trade, we aim for the price to be rejected at the H3 level before entering the trade. Stops are placed above H4 for short trades.
Breakout trade: If we want a short breakout trade, we must make sure that the price falls below the L3 level before entering the trade. Stops are placed above H3 or H4 for short trades.
Long:
Bounce-Trade: If we want a long trade, we aim for the price to rise below the L3 level before entering the trade. Stops are placed under L4 for long trades.
Breakout trade:
If we want a long breakout trade, we must ensure that the price rises above the H3 level before entering the trade. Stops are placed below L3 or L4 for long trades.Shown: GBP/JPY M30 Chart - Admiral Markets MT4 - Disclaimer: Charts for financial instruments in this article are for illustrative purposes and do not constitute trading advice or an invitation to buy or sell financial instruments provided by Admiral Markets (CFDs, ETFs, Shares). Past performance is not an indication of future performance.
Scenario #1: The Market Opens Outside H3 and L3 Levels
If the market opens outside of H3 and L3, we should wait until the market moves back through the L3 or H3 level - as we will then trade with the trend and once again place a stop loss somewhere before the appropriate H4 or L4 level. This usually happens when the market opens with a gap. This can be a slightly dangerous scenario if the gap is to close. However, some traders use it in the form of S&R scalping, which only targets 10-15 pips.
The open price is between H3 and H4 (long trades only):
- Buy when the price rises above H4
- Stop Loss just below H3;
- Target is H5.
The open price is between L3 and L4 (only for short trades):
- Sell when the price falls below L4;
- Stop loss is only L3;
- The target is L5.
Murray Math Lines (MML)
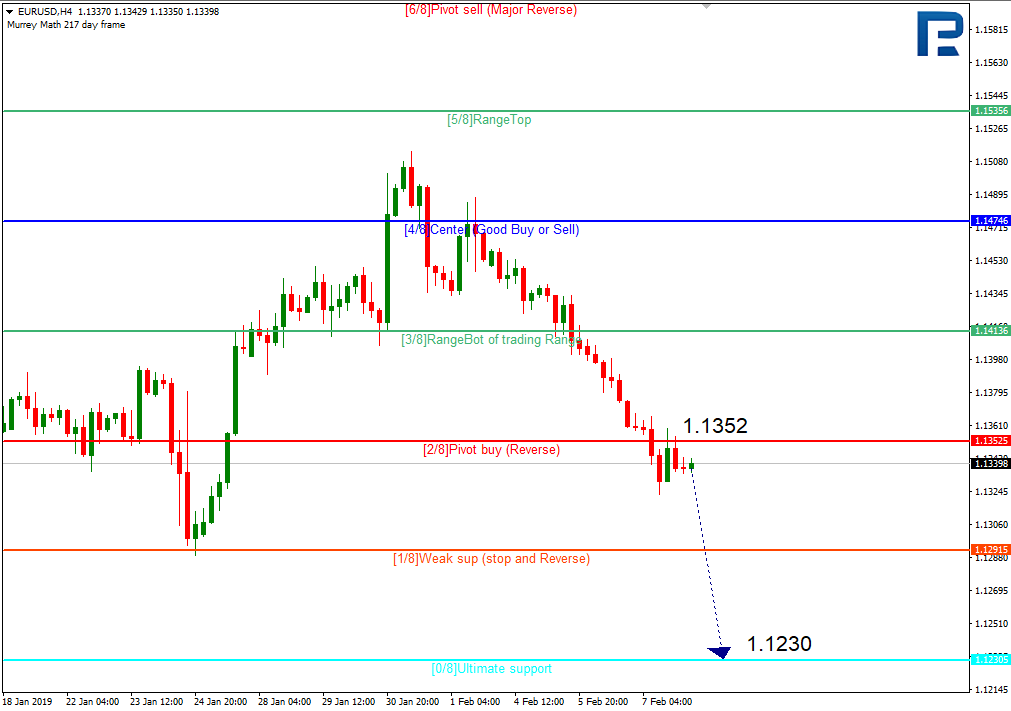
According to the Gann theory, prices usually move in the form of octaves. In Murrey Math lines this is represented by 1/8. These 1/8 are points of price support and resistance. If we equip these octaves with different characteristics of price action, each Murrey math line has its own characteristic.
8/8 AND 0/8 LINES (ULTIMATE S&R)
These lines should be the hardest to penetrate on the way up and offer the greatest support on the way down. (Prices are likely to reject these lines in the first test and will hardly penetrate them on the way up).
7/8 LINE (WEAK, STANDSTILL AND REVERSAL)
This line is a weaker resistance. If prices rise too quickly and stop at this line, they could fall quickly again. If the price does not stop at this line, it should rise to the 8/8 line.
6/8 AND 2/8 LINES (REVERSE PIVOTS)
These two Murrey lines are the second most important in their ability to force prices to reverse in the opposite direction after the 4/8 line.
5/8 LINE (THE UPPER END OF THE TRADING RANGE)
Prices usually spend 40% of the time moving between lines 5/8 and 3/8. If prices move above the 5/8 line and stay above it for some time, the market should sell at a premium point compared to what you want to pay for it. In the "premium area", prices could stay above that line. However, if the price falls below the 5/8 line, there is a chance that it will continue to fall and look for support at a lower level.
4/8 LINE (MAIN SUPPORT / RESISTANCE)
This line offers the highest level of support and resistance. This line acts as solid support when prices are above it and as dominant resistance when prices are below it. This price level is one of the best levels to place a new sell and buy.
3/8 LINE (THE LOWER END OF THE TRADING RANGE)
If the price is below this line and rises, this level acts as a resistance and should be difficult to penetrate. If the price goes above this line and stays above it for some time, we could say that the tendency is for the price to stay above this line and spend about 40%* of the time moving between this line and the 5/8 line.
1/8 LINE (WEAK LEVEL, STOP AND REVERSAL)
This line has a low level of support. If the price falls too quickly towards these levels and stops at this line, it could reverse quickly. But if the price doesn't stop at this level, it could fall to the 0/8 line. There are standard principles for Murrey Math Lines (MML), and traders use them to define clear S&R levels for their trading strategies. Some MML S&R indicators use +1/8, +2/8 and -1/8 and -2/8 octaves. When these octaves are broken, the MML S&R indicator prints a new octave.









